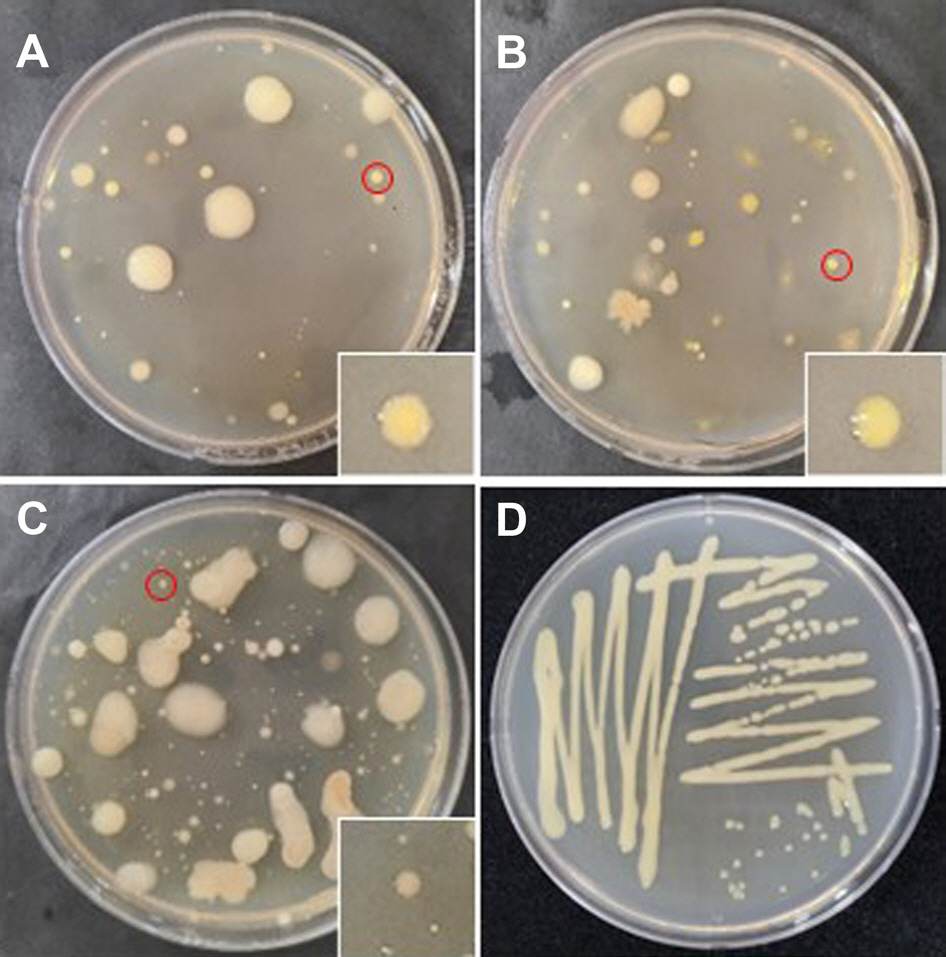
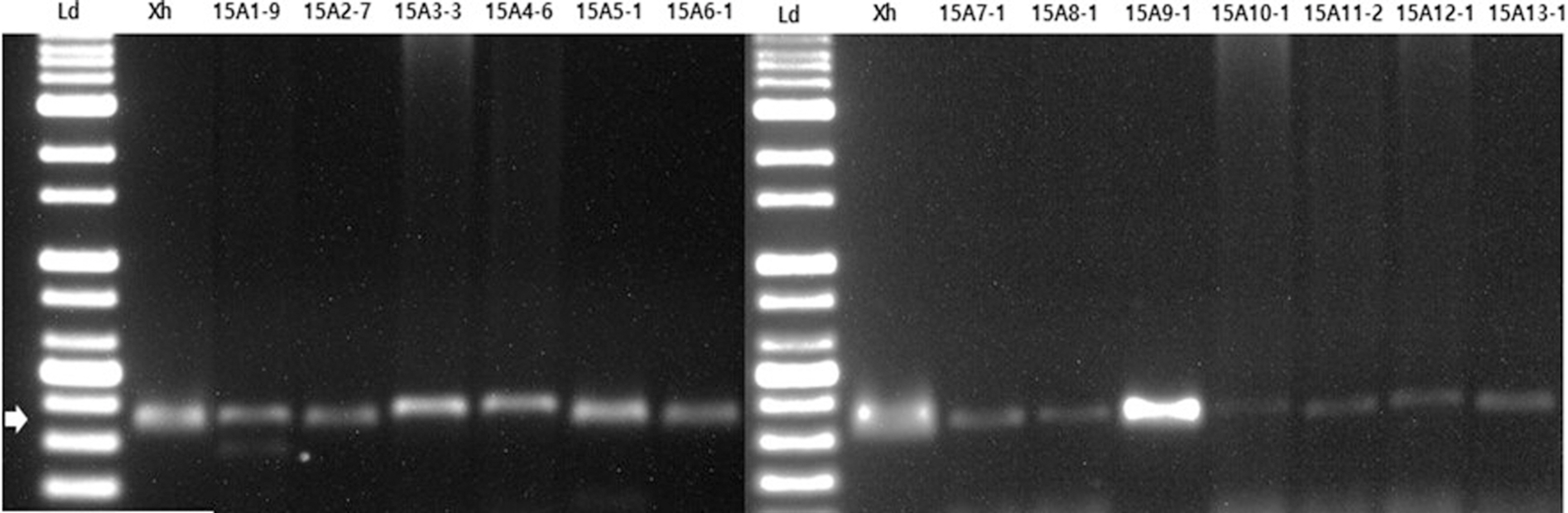
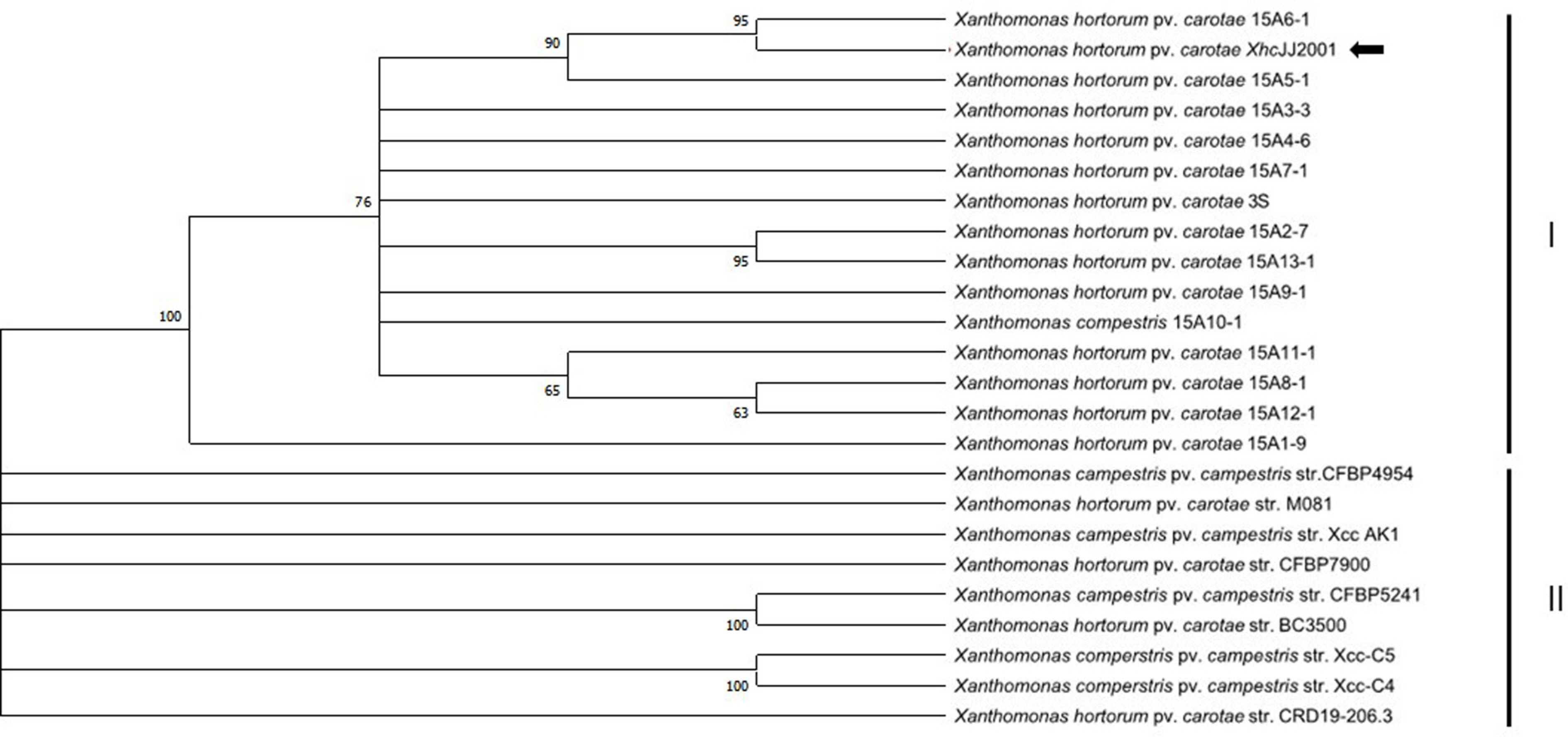
Amann, R. I., Ludwig, W. and Schleifer, K. H. 1995. Phylogenetic identification and
in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation.
Microbiol. Rev. 59: 143-169.


Bastas, K. K., Butt, H. and Gur, A. 2021. Seedborne bacteria of or-ange and black colour carrots in Turkey.
Int. J. Phytopathol. 10: 203-214.

Catara, V., Cubero, J., Pothier, J. F., Bosis, E., Bragard, C., ├Éermi─ć, E. et al. 2021. Trends in molecular diagnosis and diversity studies for phytosanitary regulated
Xanthomonas.
Microorganisms 9: 862.



Dia, N. C., Morini├©re, L., Cottyn, B., Bernal, E., Jacobs, J. M., Koebnik, R. et al. 2022.
Xanthomonas hortorum - beyond gardens: current taxonomy, genomics, and virulence repertoires.
Mol. Plant Pathol. 23: 597-621.



Dowson, W. J. 1939. On the systematic position and generic names of the Gram-negative bacterial plant pathogens. Zentralbl. Bak-teriol. Parasitenkd. Infektionskr. 100: 177-193.
Dupas, E., Durand, K. and Jacques, M.-A. 2023.
Analysis of the worldwide diversity of Xanthomonas hortorum pv. carotae, the agent of bacterial blight of carrot, reveals two distinct populations Preprint at
https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.21.537781
Du Toit, L. J., Derie, M. L., Christianson, C. E., Hoagland, L. and Si-mon, P. 2014. First report of bacterial blight of carrot in Indiana caused by
Xanthomonas hortorum pv.
carotae.
Plant Dis. 98: 685.

Gilbertson, R. L. 2002. Bacterial leaf blight of carrot. In: Compen-dium of Umbelliferous Crop Diseases, eds. by R. M. Davis and R. N. Raid, pp. 11-12. American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul, MN, USA.
G├│mez, J. L. P., Shima, M., Monterde, A., Navarro, I., Barb├®, S. and Marco-Noales, E. 2021. First report of bacterial leaf blight caused by
Xanthomonas hortorum pv.
carotae on carrots in Spain.
Plant Dis. 105: 2712.

Hong, Y.-S., Choi, H. J., Lee, I., Lim, Y.-J., Park, S. W., Nam, B. W. et al. 2020. Investigation of prohibited seed-borne plant pathogenic bacteria in Korea.
Res. Plant Dis. 26: 134-143. (In Korean)

Hornsby, R. L., Jensen, A. E., Olsen, S. C. and Thoen, C. O. 2000. Se-lective media for isolation of
Brucella abortus strain RB51.
Vet. Microbiol. 73: 51-60.


International Seed Testing Association. 2014. International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods. Detection of Xanthomonas hortorum pv. carotae on Daucus carota (carrot). International Seed Testing Association, Bassersdorf, Switzerland. pp. 12 pp.
Kendrick, J. B. 1934. Bacterial blight of carrot. J. Agric. Res. 49: 493-510.
Kim, Y. S. and Jang, S.-J. 2012. Basic concepts of bacterial taxonomy.
Korean J. Clin. Microbiol. 15: 79-87.

Koehler, A., Karch, H., Beikler, T., Flemmig, T. F., Suerbaum, S. and Schmidt, H. 2003. Multilocus sequence analysis of
Porphyromo-nas gingivalis indicates frequent recombination.
Microbiology 149: 2407-2415.


Kuan, T.-L., Minsavage, G. V. and Gabrielson, R. L. 1985. Detection of
Xanthomonas campestris pv.
carotae in carrot seed.
Plant Dis. 69: 758-760.

Kwon, M., Ryu, K.-Y., Kim, J.-S. and Shin, G.-Y. 2007. Occurrence pat-tern of pests in carrot fields and effect of plant debris removal after harvest at highland area. Korean J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 25: 316-321. (In Korean)
Lee, S., Park, J., Lee, O.-M. and Shin, Y.-G. 2013. Plant quarantine isolated cultivation system in Korea and results of recorded in 2005-2012.
Korean J. Agric. Sci. 40: 281-287.

Meng, X. Q., Umesh, K. C., Davis, R. M. and Gilbertson, R. L. 2004. Development of PCR-based assays for detecting
Xanthomonas campestris pv.
carotae, the carrot bacterial leaf blight pathogen, from different substrates.
Plant Dis. 88: 1226-1234.


Merda, D., Briand, M., Bosis, E., Rousseau, C., Portier, P., Barret, M. et al. 2017. Ancestral acquisitions, gene flow and multiple evolutionary trajectories of the type three secretion system and effectors in
Xanthomonas plant pathogens.
Mol. Ecol. 26: 5939-5952.



Morini├©re, L., Burlet, A., Rosenthal, E. R., Nesme, X., Portier, P., Bull, C. T. et al. 2020. Clarifying the taxonomy of the causal agent of bacterial leaf spot of lettuce through a polyphasic approach reveals that
Xanthomonas cynarae Tr├®baol et al. 2000 emend. Timilsina et al. 2019 is a later heterotypic synonym of
Xanthomonas hortorum Vauterin et al. 1995.
Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 43: 126087.


Myung, I.-S., Yoon, M.-J., Lee, J.-Y., Kim, G.-D., Lee, M.-H., Hwang, E.-Y. et al. 2014. First report of bacterial leaf blight of carrot caused by
Xanthomonas hortorum pv.
carotae in Korea.
Plant Dis. 98: 275.

Nishiyama, K., Fukunishi, T., Terada, T. and Ezuka, A. 1979. Bacterial blight of carrot caused by Xanthomonas carotae, a bacterial disease new to Japan. Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Jpn. 45: 683-688.
Pfleger, F. L., Harman, G. E. and Marx, G. A. 1974. Bacterial blight of carrots: interaction of temperature, light and inoculation procedures on disease development of various carrot cultivars.
Phytopathology 64: 746-749.

Palleroni, N. J., Hildebrand, D. C., Schroth, M. N. and Hendson, M. 1993. Deoxyribonucleic acid relatedness of 21 strains of
Xanthomonas species and pathovars.
J. Appl. Bacteriol. 75: 441-446.

Ritchie, D. F. and Dittapongpitch, V. 1991. Copper- and strepto-mycin-resistant strains and host differentiated races of
Xanthomonas campestris pv.
vesicatoria in North Carolina.
Plant Dis. 75: 733-736.

Yoo, Y. B. and Hyun, G. N. 1995. Economic analysis on the export competitiveness of Jeju fresh carrots to Japan. Soc. Dev. Rev. 11: 119-149.
Young, J. M., Dye, D. W., Bradbury, J. F., Panagopoulos, C. G. and Robbs, C. F. 1978. A proposed nomenclature and classification for plant pathogenic bacteria.
N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 21: 153-177.