 |
 |
| Res. Plant Dis > Volume 26(1); 2020 > Article |
|
요 약
2016년 콩을 재배하는 포장에서 마름 증상에 의한 콩의 피해가 심하게 발생하였다. 유묘기 때에는 잘록 증상과 자엽에 갈색 또는 검은색의 반점이 나타나기 시작하다가, 8월 이후 개화기에는 지상부 잎이 황화되기 시작하면서 부분적으로 갈변되었다. 이 시기에 채집한 콩의 뿌리는 생육이 많이 억제된 상태이며, 표피 가 벗겨지면서 균핵이 형성되기 시작하였다. 9월 이후부터는 지상부의 마름 증상이 더 뚜렷해졌으며 고사하기 시작하였고, 수침상 병징을 보이던 줄기에도 균핵이 형성되었다. 수확기인 10 월 중순 이후에는 줄기의 표피가 벗겨지면서 피층 부위에 소립균 핵이 다량으로 형성되었다. 이런 병징으로부터 분리한 병원균은 32-35°C에서 균사 생육이 가장 양호하였고, 소립균핵의 형성은 20-28°C에서 가장 많았다. 병원균의 균학적인 형태 관찰과 internal transcribed spacer 영역 유전자의 염기서열 분석을 실시한 결과, 병원균은 Macrophomina phaseolina로 동정되었다. 또한 이쑤시개를 이용한 인공접종에서도포장에서와 같은 병징을 보였을 뿐만 아니라, 재분리에서도 동일한 병원균이 분리ㆍ동정되었다. 그 결과 이 병을 콩 균핵마름병(가칭)으로 보고하는 바이다.
ABSTRACT
Stem blight symptom of soybean was severely developed in 2016 in Hwaseong and Yeoncheon. During the seedling period, the damping-off of seedlings and the brown or black spots of cotyledons were observed. After August, the leaves began to be yellowed, and partially browned areas on leaves began to develop. After September, microsclerotia began to form even on the surface of the stems that had exhibited water-soaking symptom. After mid-October of the harvest season, the epidermis of the stem was peeled off, resulting in the formation of a large number of microsclerotia in the cortex. The pathogens isolated from these symptoms were the best in mycelial growth at 32-35°C, and the formation of microsclerotia was the most at 20-28°C. The pathogen was identified as Macrophomina phaseolina through the morphological characteristics of the pathogen and the sequencing of the internal transcribed spacer region gene. In addition, when inoculated with a soybean stem using toothpicks cultured with the pathogen, the same symptoms as seen on the soybean field occurred. When the pathogen was re-isolated at the lesion site, the same pathogen was isolated and identified as Macrophomina phaseolina. Based on the results, the disease is reported as soybean charcoal rot.
콩(Glycine max Merr.)은 된장, 간장 등 전통음식의 원료뿐만 아니라, 다양한 생리적 효과를 가지고 있기 때문에 의약, 사료, 공업용과 섬유 등의 원료로 광범위하게 사용되고 있지만, 국내 콩 재배면적과 생산량은 계속 감소하고 있다. 1981년에 201,722ha에서 256,851톤이 생산되다가, 2000년 들어오면서 재배 면 적은 86,176 ha로, 생산량은 113,196톤으로 감소하였다(Korea Statistical Information Service, 2020). 감소 추세는 계속되어 2018년의 콩 재배면적과 생산량은 50,638 ha와 89,410톤까지 하락하였다. 이처럼 콩은 재배면적과 생산량이 감소하고 있을 뿐만 아니라, 재배 기간 중에는 여러 가지 식물병원체가 침입하여 다양한 병이 발생하며 생산량이 위협당하고 있다. 전 세계 적으로 콩의 생산량을 떨어뜨리는 중요한 병으로는 시스트선충병, Rhizoctonia, Pythium 등에 의한 유묘기의 병, Macrophomina에 의한 charcoal rot, Fusarium에 의한 sudden death syndrome, Septoria에 의한 갈색무늬병 등이 보고되어 있다 (Allen 등, 2017). 국내에는 진균이 일으키는 병이 탄저병을 비롯 하여 24종, 세균이 일으키는 병이 불마름병 등 4종, 바이러스에 의한 병과 선충에 의한 병이 각각 4종과 3종씩이 보고되어 있 다(Korean Society of Plant Pathology, 2009).
국제적으로도 콩의 주요한 생산지인 미국과 캐나다 온타리오 지역의 2010년부터 2014년까지 5년간의 누적 생산량은 172억 부셸인데, 동일한 기간 동안 병으로 인한 콩 생산량 감소는 전체 생산량의 12.5%에 해당하는 21억 부셸에 달한다(Allen 등, 2017). 발생하는 주요 병은 지역에 따라서 차이가 있는데, 미국 북부 지역은 콩 시스트선충에 의한 피해가 가장 컸던 반면에, 남부 지역에서는 2010년부터 2012년까지 연 3년간 charcoal rot에 의한 피해가 가장 컸다. 미국 남부 지역에서 콩 생산량 감소의 주된 원인이 되는 charcoalrot은 Macrophomina가 일으키는 병으로, 고온 건조한 지역에서 발생이 심하다고 알려져 있다. 그런데 최근 콩 재배 기간 동안의 국내 기상 상황이 고온건 조해지는 경향을 보이고 있어, 포장에서 주요 병의 발생이 변화할 수 있다는 우려를 낳고 있다. 1980년에 11.2°C이었던 연평 균 기온이 2019년에는 13.5°C로 상승하였으며, 콩 재배 기간인 5월부터 10월까지 6개월간의 평균 강수량을 보아도 2013년부터 2017년까지 5년간은 계속 150 mm 이하를 기록하고 있다 (Korea Meteorological Administration, 2020).
기상이 고온 건조해지면서 2016년에 경기도 화성과 연천지역의 포장에서 재배하던 콩이 심하게 시드는 증상이 나타났다. 국 내에서 콩 마름 증상을 일으킨다고 보고된 병으로는 Diaporthe 에 의한 미이라병, Fusarium에 의한 시들음병, Sclerotium에 의한 흰비단병 등이 있지만(Korean Society of Plant Pathology, 2009), 전 세계 콩 주요 생산 10개국의 생산량 감소의 원인 중 네 번째로 평가될 만큼 큰 피해를 주는 Macrophomina phaseolina에 의한 charcoal rot은 알려져 있지 않은 상태이다 (Wrather 등, 1997). 이 병은 병원균이 콩 뿌리를 침입한 후, 세 포간극을 통해서 유관속 부위의 물관까지 이동하여 유관속 조직을 기계적으로 폐쇄시켜 시들음과 마름 증상이 발생하는 병이다(Smith와 Wyllie, 1999). 발병 후기가 되면 이 병의 특징적인 표징인 소립균핵(microsclerotia)이 뿌리와 줄기조직에 다량 형성된다(Gupta 등, 2012). 이 병원균에 감염된 기주는 초기에는 뚜렷한 증상을 나타내지 않지만, 고온건조한 환경조건이 지속될 경우 시들음 증상과 괴사증상이 촉진되는 것으로 알려져 있다(Twizeyimana 등, 2012).
본 연구는 2016년 고온건조한 기상 조건에서 시들음 증상을 보인 콩을 경기도 화성과 연천의 콩 재배 포장에서 채집하여,시들음 증상의 원인이 되는 병원균을 분리하여 유전자 수준에서 동정하고, 균학적 특징과 병원성 등을 조사하여 보고하고자한다.
2016년 7월부터 10월까지 경기도 화성과 연천지역에서 시들음 증상을 보이는 콩을 채집하였다. 수집한 병든 콩에서 병원균을 분리하기 위하여 감염된 조직을 잘라 1%차아염소산나트륨(NaOCl) 용액으로 1분간 표면 살균하고 살균수로 3회 세척하였다. 멸균된 여과지에서 물기를 제거한 다음, potato dextrose agar (PDA, Difco, Detroit, MI, USA) 배지위에 올려놓고 28°C에서 3일간 배양하였다. 병든 조직에서 자라나온 균사의 선단부에서 균사 조각을 떼어 PDA 사면배지에 접종한 후 4°C에서 보관하며 실험에 사용하였다. 또한 콩 이외의작물 중에서 참깨, 팥, 녹두, 땅콩 등에서 시들음 증상을 보이는개체를 채집하고 분리되는 병원균을 형태적으로 동정하였다.
병원균 배양에 적합한 배지를 조사하기 위해서 분리한 M. phaseolina HSW16-141 균주를 28°C의 PDA 배지에서 3일간 배양한 후, 균사 선단부에서 직경 7 mm의 균사 조각을 떼어내어 새로운 PDA 배지에 접종하고, 정해진 온도(20°C, 25°C, 30°C, 32°C, 35°C, 37°C, 40°C)에서 배양하며 균총의 직경을 조사하였다.
Chidambaram과 Mathur (1975)의 방법에 따라 분생포자를 형성시켰다. 보리 잎을 적당한 크기로 자른 후 흐르는 물에 세척하여 건조시킨 후, 121°C에서 15분간 멸균하였다. 멸균한 보리 잎은 미리 준비해 둔 1.5% 물한천배지에 올린 후, PDA 배지에서 48시간 배양한 병원균 균총 선단에서 균사 조각을 떼어 접종하였다. 병원균을 접종한 보리 잎은 30°C에서 12시간씩 광/암 조건을 유지하며 7일간 보관하고,잎 위에 형성된 분생포자각과 분생포자 그리고 소립균핵 등을관찰하였다.
병원균의 병원성 검정은 Gopala 등(2016)의실험 방법을 개선하여 실시하였다. M. phaseolina HSW16-141 균주를 32°C의 PDA 배지(암조건)에서 3일간 배양하였다. 이쑤 시개를 12 mm (길이)로 자른 후 121°C에서 30분 동안 1일 간격 으로 총 2회 멸균하였다. 새롭게 준비한 PDA 배지(300 µg/ml의 streptomycin을 첨가)에 멸균한 이쑤시개 5개를 올려놓은 다음, M. phaseolina HSW16-141의 균총 선단에서 직경 7 mm의균사 조각을 잘라내어 하나의 페트리 접시당 7개씩 접종하였다. 병원균은 32°C 암조건에서 7일간 배양하여, 접종원으로 사용하였으며, 대원콩을 온실에서 재배하여 병원성 실험에 사용 하였다. 재배에 사용한 원예용 상토는 121°C에서 60분간 1일 간격으로 총 2회 멸균한 후 포트(직경, 10 cm; 높이, 9 cm)에 담고, 2% NaOCl에 2분간 표면소독한 대원콩 종자를 1립씩 파종하여 재배하였다. 콩의 초생잎이 완전히 전개되고 제1본엽이 출현하 였을 때, 접종원으로 준비한 이쑤시개로 지제부가 관통하도록 찔러 병원균을 접종하고 멸균한 상토를 1 cm 가량 덮어주었다. 무처리구는 병원균을 접종하지 않은 멸균한 이쑤시개를 사용 하여 동일하게 실험을 수행하였다. 병원균을 접종한 콩은 32°C 의 생장상(광/암, 12 hr/12 hr; 습도, 50% 이상)으로 옮겨 30일간 재배하며 발병을 유도하였다.
경기도 화성과 연천의 병든 콩에서 분리한 HSW16-141, HSB16-159, HSS16-165와 YSW16-175, YSB16-178, YSS16-176 등 총 6균주를선발하여 ITS 유전자 염기서열 분석을 실시하였다. NucleoSpin PlantⅡ (MACHEREY-NAGEL, Duren, Germany) 키트를 사용하여 동결건조시킨 병원균의 균사로부터 genomic DNA를 추출 하고, ITS4 (5'-TCC TCC GCT TAT TGA TAT GC-3')과 ITS5 (5'-GGA AGT AAA AGT CGT AAC AAG G-3') 프라이머를 사용하여 ITS영역을 증폭하였다. 유전자의 증폭은 95°C에서 4분 처리하고, 94°C에서 변성 과정 30초, 48°C에서 결합 과정 60초, 72°C에서 신장 과정 60초의 주기를 총 30회 실시하였으며, 마지막 신장 과정은 72°C에서 7분간 실시하였다. 증폭된 PCR 산물은 1.5% agarose gel에서 전기영동하여 밴드를 확인하고, PCR purifica-tion kit (eCube PCR Purification Kit, Phile Korea, Seoul, Korea) 를 이용하여 정제하였다. 정제한 DNA는 Macrogen (Seoul, Korea)에 염기서열 분석을 의뢰하였으며, 분석된 염기서열은nBLAST 프로그램으로 GenBank에 등록되어 있는 Macrophomina속 곰팡이 균주와 콩 수확기에 발생하는 식물병의 병원균 균주와 비교하였다.
콩 유묘기에 지제부에서 수침상의 병징이 형성되다가 모잘록 증상으로 발전하였으며, 출아한 떡잎에 검은 반점이나타나기도 하였다(Fig. 1A, B). 개화기(2016년 8월 17일)에 채집한 병든 콩은 지상부 잎이 황화되기 시작하고 부분적으로 갈변하는 부위들이 나타나기 시작하였다(Fig. 2A). 채집한 병든 콩의 뿌리 생육은 많이 억제되어 있었는데, 잔뿌리가 탈락되며뿌리 부위의 표피가 벗겨지면서 균핵이 형성되기 시작하였다(Fig. 2B). 개화기 이후 9월 12일경에는, 지상부에 마름 증상이뚜렷하게 나타나기 시작하였고, 뿌리계의 주근이 잘려나가면서, 고사하였다(Fig. 3). 또한 수침상의 증상을 보이던 줄기에도소립의 균핵이 형성되었다. 수확기인 10월 12일 경에 병징을 보면, Fig. 4에서 보는 것과 같이 원거리의 포장에서도 마름 증상이 나타난 부위가 뚜렷하게 구별되었다. 또한 병든 콩의 줄기 표면과 지제부의 표피가 벗겨진 내부 피층 부위에 형성된 균핵을뚜렷하게 관찰할 수 있었다. 병든 개체의 줄기를 세로로 절단할 경우 유관속 부위에 다량의 균핵이 형성된 것을 볼 수 있었다 (Fig. 4). 콩에서의 병징은 M. phaseolina가 블루베리를 침입할 때 지상부의 잎이 시들고, 줄기와 뿌리는 갈변하면서 시드는 증상과 유사하였다(de los Santos 등, 2019).결국, 포장에서 M. phaseolina가 콩을 침입하게 되면 콩잎이 시들면서 조기에 쇠약해지고 식물체가 은회색으로 변색되어 죽었다. 초기에는 뿌리, 지제부, 줄기에 수침상의 증상이 나타나며, 병이 진전되면서 뿌리와 지제부의 표피조직이 벗겨지고, 그 속에 검은색의 소립균핵이 형성되기 시작하였다. 콩의 품종에 따라서 표피가 터지면서 섬유조직이 갈라지는 증상이 나타나기도 하였다. 이러한 병징을 보이는 기주는 건전한 콩과는 다르게 뿌리와 지제부가 썩고 잔뿌리가 거의 없어 잘 뽑히며, 꼬투리가 제대로 여물지 않아 대부분 결실이 되지 않았다.
병든 콩 조직에서 병원균을 분리한 결과, Macrophomina, Phomopsis, Colletotrichum, Botryospaeria, Cercospora속의 식물병원곰팡이가 분리되었으며, Macrophomina의 분리빈도는 15.2%이었다(Table 1). 콩 이외에도 참 깨와 팥에서 Macrophomina는 각각 26.7%와 9.1%씩 분리되었다. 하지만 콩 이외의 작물은 채집한 시료의 수가 적었던 관계로 더 세밀한 조사를 실시할 필요가 있다.
분리한 병원균 M. phaseolina HSW16-141 균주를 30°C의 PDA 배지에서 배양하면 균총의 균사 색깔이 처음에는 흰색을 띄다가 배양기간이 경과하면서 회색 내지 검은색으로 변하였다. 배양하고 5일이 지나면서부터 PDA 배지 상에서 검정색의 구형인 소립균핵이 형성되기 시작하였으며, 평균 직경은 91 µm (직경 범위, 61-124 µm)이었다. 블루베리의 병든 조직에서 분리한 병원균도 30°C의 암상태에서 배양하면 검고 둥근 소립균핵을 형성하는데, 소립균핵의 크기는 평균 98 µm (61-128 µm)로 콩에서 분리한 소립균핵과 형태적으로 매우 유사하였다(de los Santos 등, 2019). 분생포자와 분생포자각은 PDA 배지상에서는 형성되지 않았다. 하지만 멸균한 보리 잎을 물한천 배지 위에 올려놓고 보리잎 위에 M. phaseolina HSW16-141을 접종하여 배양하였을 때, 검정색의 둥근 분생포자각이 형성되었으며, 분생포자각 안에는 끝이 둥글고 타원형이며 투명한 단포자인 분생포자가 대량으로 형성되었다(Fig. 5). 분생포자각의 평균 직경은 221 µm (157-301 µm)이었으며, 분생포자의 장경과 단경 은 24 µm (16-33 µm)와 11 µm (9-13 µm)이었다. 보리잎에서도 검정색의 구형인 소립균핵이 형성되었다.
M. phaseolina HSW16-141을 PDA 배지에 접종하고 각각의 온도에서 2일간 배양한 후 균총의 직경을 조사한 결과, 35°C에 서 8.2 cm로 가장 빠르게 생장하였고, 30°C와 37°C에서는 6.1 과 6.3 cm로 생장 속도가 저하되었다. 일반적인 식물병원곰팡 이의 생장 적온으로 알려진 20°C, 25°C, 28°C에서 균사 생장 정도는 4.1, 5.0, 5.6 cm로 저조하였다(Fig. 6). 중국의 faba bean에 서 분리한 M. phaseolina FMP8-1, FMP8-2, FMP8-4와 같은 균주는 본 연구에서 사용한 콩에서 분리한 균주와는 다르게 28° C의 PDA 배지에서 12시간 광을 조사하며 배양하였을 때 생장 이 빨랐다(Sun 등, 2019). 이런 결과를 보면 국내에서 분리하는 M. phaseolina의 생리ㆍ유전적인 다양성을 조사해야 할 필요성이 있다고 생각한다.
ITS 염기서열 분석을 위해서 ITS4와 ITS5 프라이머로 M. phaseolina 균주들의 유전자를 증폭하여 580 bp의 증폭산물을 얻었다. Cummings와 Bergstrom (2013) 은 미국 뉴욕주에서 콩에 charcoal rot 증상을 일으키는 Mp001NY12 균주로부터 ITS1과 ITS4 프라이머를 사용하여 ITS 영역의 유전자를 증폭하고 염기서열을 분석한 결과, M. phaseolina와 100% 일치하였다고 보고하였다. Sun 등(2019)도 역시 faba bean에서 나타나는 charcoal rot의 원인균을 분리하여 유전자 수준에서 동정을 실시하였는데, ITS4와 ITS5 프라이머를 사용하여 약 600 bp의 ITS 영역 유전자를 증폭하였으며, 이 산물의 염기서열을 분석한 결과, M. phaseolina와 99-100% 일치하였다. 본 연구에서도 콩에서 분리한 6균주의 ITS 영역 염기 서열을 NCBI의 GenBank에 등록된 M. phaseolina의 염기서열과 비교한 결과, 100% 일치하였다. M. phaseolina의 ITS 염기서 열의 계통분석을 통해서 M. phaseolina는 Botryosphaeriaceae 과에 속하는 Botryosphaeria sp.와는 근연관계에 있으나, 콩 수확기에 발생하는 Diaporthe, Colletotrichum, Calonectira 등과 는 뚜렷한 차이가 있음을 알 수 있었다(Fig. 7).
병원균을 접종하여 준비한 이쑤시개를 이용한 상처 접종에서 콩은 접종한 지 45일경부터 병징이 나타났다. 포장에서 관찰한 바와 같이 콩의 지제부에 수침상 병징이 나타나다가 갈색 내지 검은색으로 변색되기 시작하였으며, 병이 진행되면서 콩의 줄기에서 검은색의 소립균핵이 형성되었고 결국 시들어 고사하였다. 또한 병든 부위에서 접종한 병원균과 동일한 M. phaseolina를 재분리할 수 있었다(Fig. 8).
M. phaseolina가 침입하여 병이 발생할 경우 콩의 수확량과 품질이 현저하게 감소하였다. 대원콩 을 수확한 후, Fig. 9에서 보는 것과 같이 건전한 콩 종자와 병 10A).해서 콩 종자의직경을 조사하였다. 건전한 콩 종자는 직경이 8 mm 이상 종자가 26%, 7 mm 이상부터 8 mm 이하가 72%, 6 mm 이상이고 7mm 이하인 종자가 2%인데 비하여, 병든 콩 종자의 경우에는 8mm 이상인 종자는 없고 7 mm 이상이며 8 mm 이하인 종자가12%, 6 mm 이상이며 7 mm 이하인 것이 63%, 5 mm 이상이며6 mm 이하인 것이 23%, 그리고 4 mm 이상이며 5 mm 이하인 종자도 2%나 되었다(Fig. 10B). 이처럼 M. phaseolina는 콩의 생 산량뿐만 아니라 수확한 콩의 품질에도 영향을 미쳤다. 국내에서는 Yu와 Park (1980)이 참깨 종자에서 분리한 M. phaseolina의 병원성을 보고하였으며, Sung 등(1980)은 병든 콩의 줄기나 뿌리에서 M. phaseolina를 분리하고 콩에 대한 병원성을 확인하였다. Yu와 Park (1982)은 한국산 주요작물에서 종자전염성 진균에 대해 조사를 실시하면서 참깨 시료에서 0.5-8.5% 비율로 M. phaseolina를 검출하였으며, Yum과 Park (1989)은 검은콩으로부터 평균 0.08%로 M. phaseolina를 검출 하였다고 보고하였다. M. phaseolina는 종자전염과 토양전염을 하고, 토양 속에서 2-15년 동안 생존이 가능하며(Short 등, 1980), 소립균핵은 일차 전염원의 역할을 한다고 알려져 있다 (Gupta 등, 2012; Kaur 등, 2012). 따라서 최근 들어 국내 콩 재배 포장에서 발생하는 M. phaseolina에 의한 병은 병원균이 이미 토양 속에 존재하고 있었으며, 최근 병원균의 생장에 적합한 고온 건조한 날씨가 지속되면서 병이 발생한 것으로 판단되어진다. 이미 오래 전에 Yum과 Park (1989)이 M. phaseolina의 종자 전염을 보고하였고, 요즈음 변화하는 기상 조건으로 인하여 포장에서 M. phaseolina에 의한 병 발생이 증가하고 있는 것을 보면, 포장에서 발생 유무와 병원균의 분포, 그리고 병 발생 생태 등에 대한 향후 조사가 필요할 뿐만 아니라, 콩 종자의 생산과 보급 측면에서도 많은 주의가 필요한 상태이다.이상의 결과에서 보는 것과 같이 최근 기후변화에 따른 고온 건조한 조건에서 콩에 나타나는 마름 증상이 M. phaseolina에 의한 것임을 보고하면서, 콩에서 발생한 M. phaseolina에 의한 마름 증상을 콩 균핵마름병으로 명명하고자 한다.
Acknowledgments
This research was carried out with support from the Rural Development Administration project (project title; Investigation of plant diseases caused by Macrophomina sp. and classification and identification of pathogen through DNA sequence analysis (PJ014956022020)), and we appreciate the support.
Fig. 1
Damping off in soybean. (A) Water-soaked symptoms near the soil ground of soybean seedlings. (B) Damping off in soybean seedlings and black spots on cotyledon leaves.

Fig. 2
Diseased soyeans collected during the flowering period. (A) Diseased soybeans collected during the flowering period began to yellowing in the ground leaves and partially browning areas appeared. (B) The growth of the roots of the diseased soybeans was largely suppressed. As the roots were eliminated, the epidermis of the roots was peeled off, and the sclerotia formed. The arrow points to the root part where the epidermis is peeled off.

Fig. 3
Blight symptom of soybean. Soybeans began to show the blight throughout the plant (A), and tap root were cut off and died (B, C).
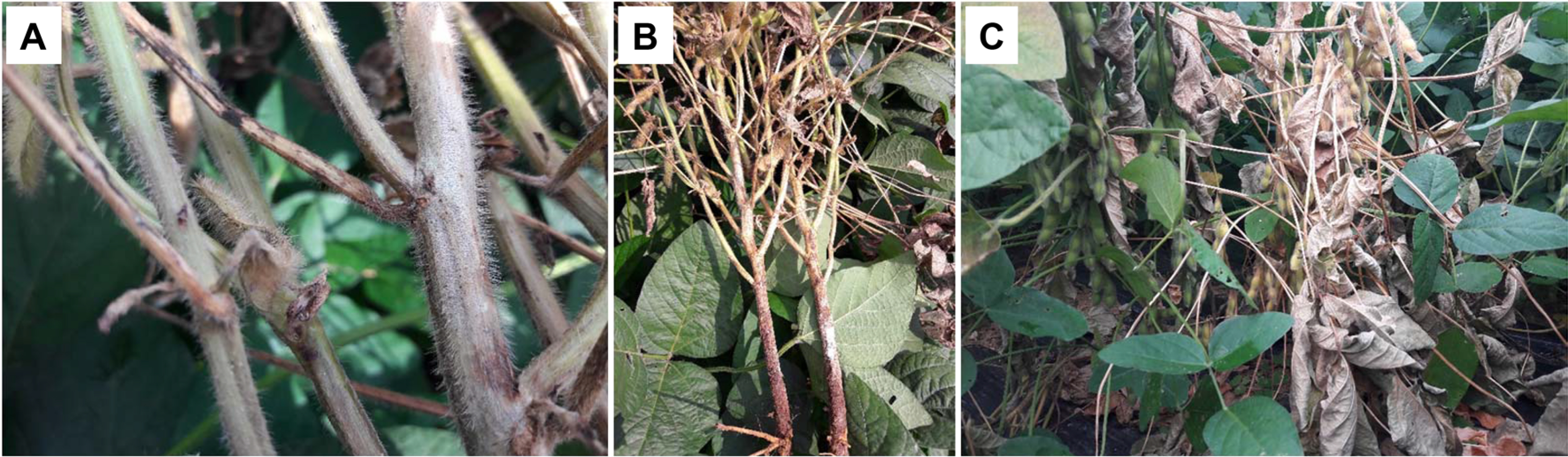
Fig. 4
Soybean field (A) where beans are dead due to blight and symptoms in the late growth period (B-D). It was easy to see that some of the soybean fields were dying from dryness. Sclerotia formed on the stem surface of the diseased soybean and on the inner cortex where the epidermis of the stem was stripped were clearly observed.

Fig. 5
Macrophomina phaseolina produced on barley leaves on an water agar medium. (A) Conidia and pycnidium on a barley leaf (×200). (B) Pycnida and macrosclerotia formed in water agar leaf medium (×45).
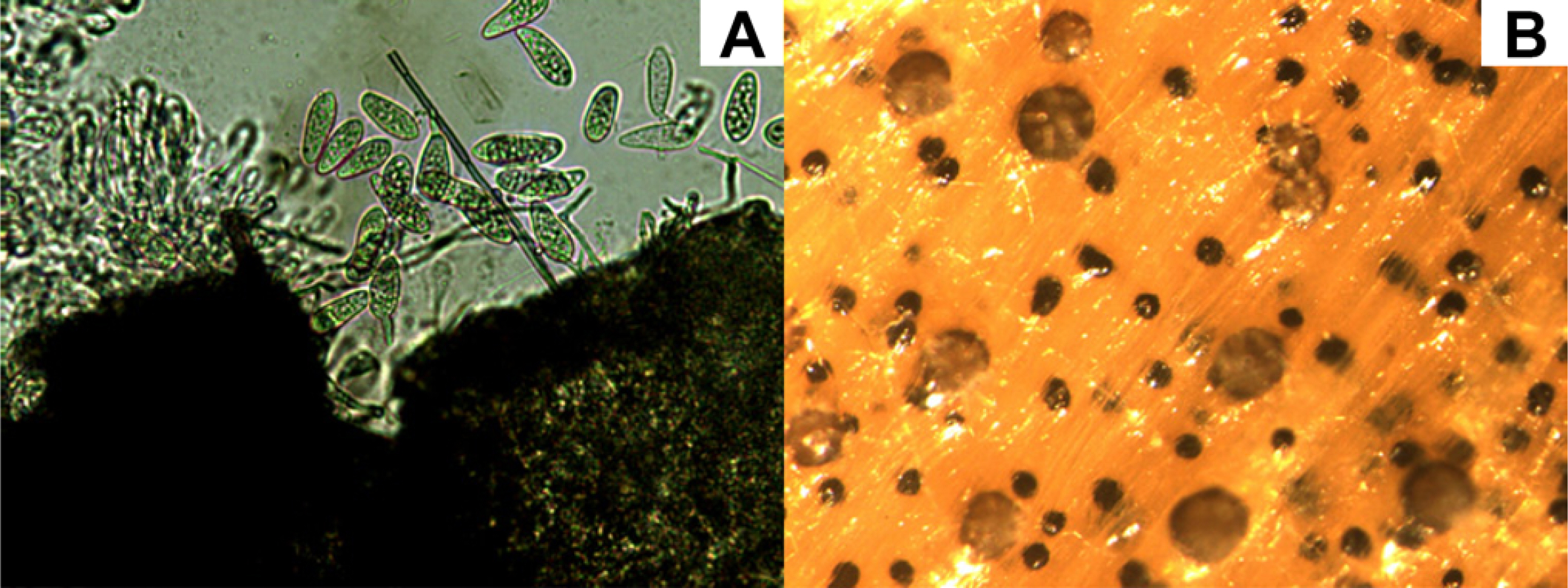
Fig. 6
Mycelial growth of Macrophomina phaseolina isolated from infected soybean plants on potato dextrose agar at indicated temperatures. Colony diameter was measured after incubation for 2 days under the dark condition. The colony diameter was the average of three replications. The different letters on the bars are statistically significant based on Duncan multiple range test (P≤0.01).
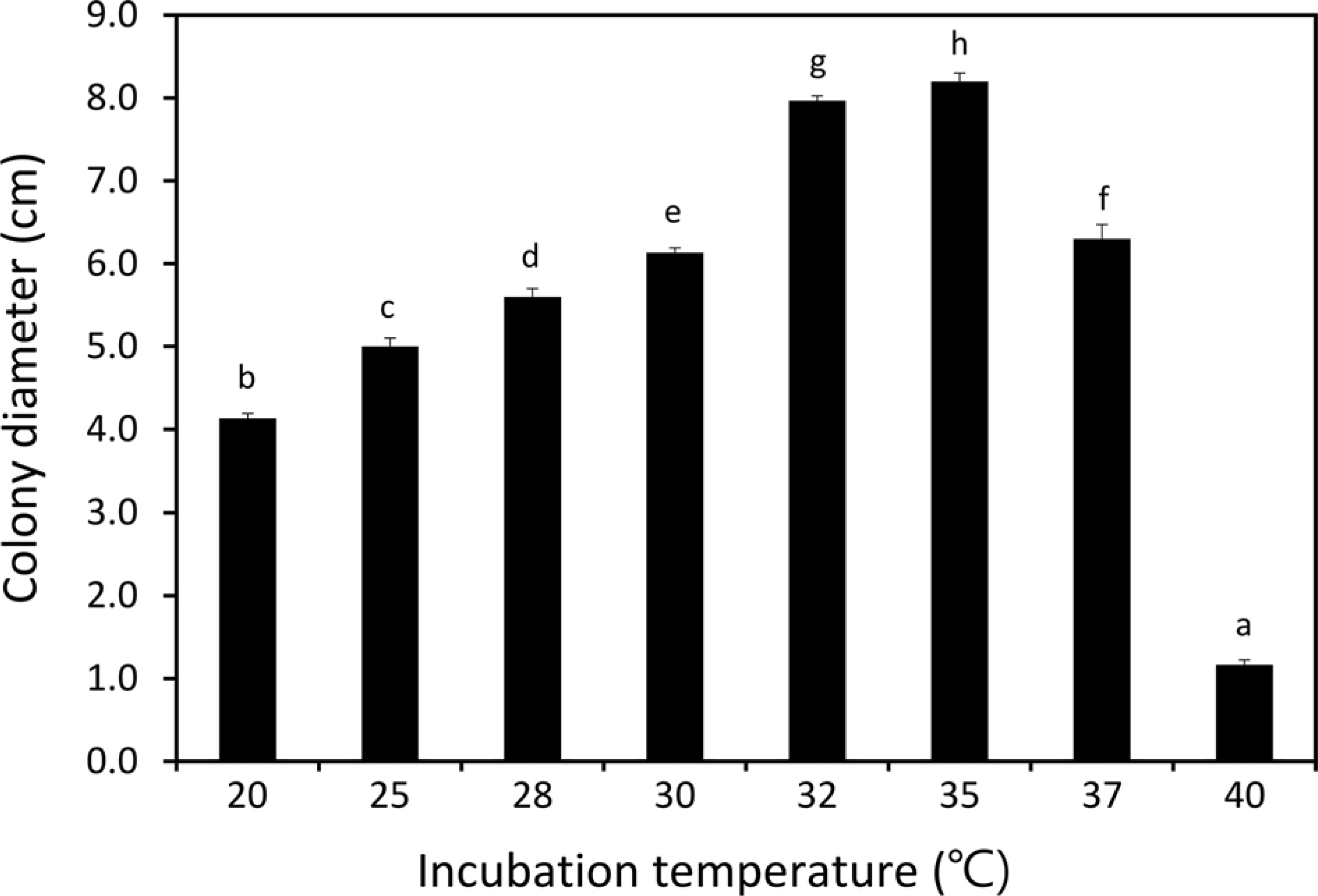
Fig. 7
Phylogenetic tree of the Macrophomina phaseolina isolates constructed from the multiple alignments of internal transcribed spacer rDNA sequences, using neighbour-joining method and 2,000 boots.

Fig. 8
Pathogenicity test of Macrophomina phaseolina isolated from infected soybean. (A) Stem blight caused by artificial inoculation of the pathogen, as Macrophomina phaseolina isolated from infected soybean. Left row; non-inoculated soybeans, right row; inoculated soybeans. (B) A typical sign showing macrosclerotia on lesions after an artificial inoculation. (C) The colony of Macrophomina phaseolina reisolated from the symptoms on stems of soybean developed by the artificial inoculation.
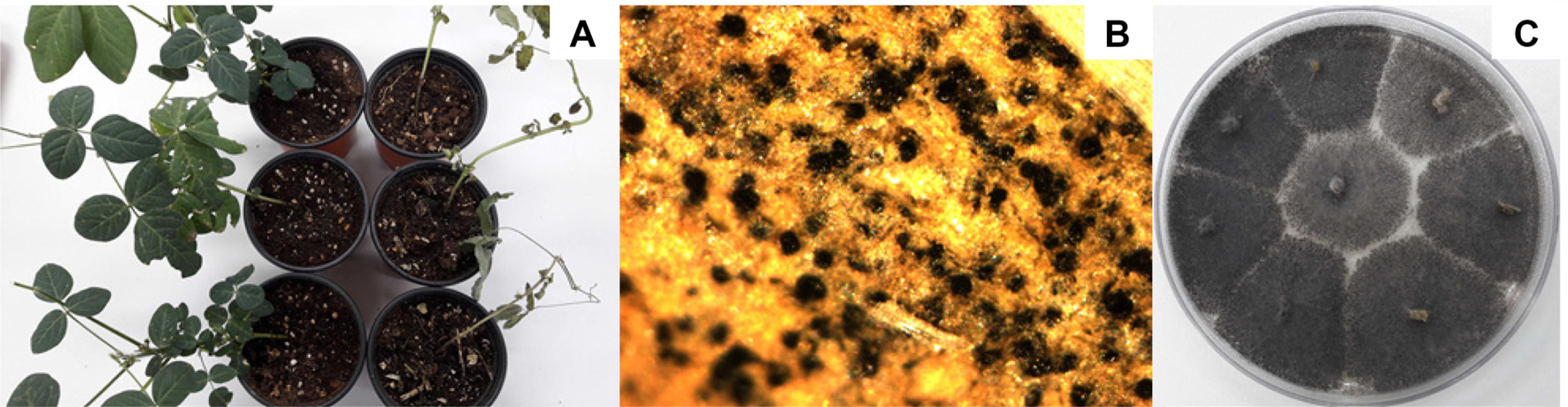
Fig. 9
Harvested soybeans. Left rows were soybeans harvested from healthy soybeans, and right rows were it from infected soybeans.
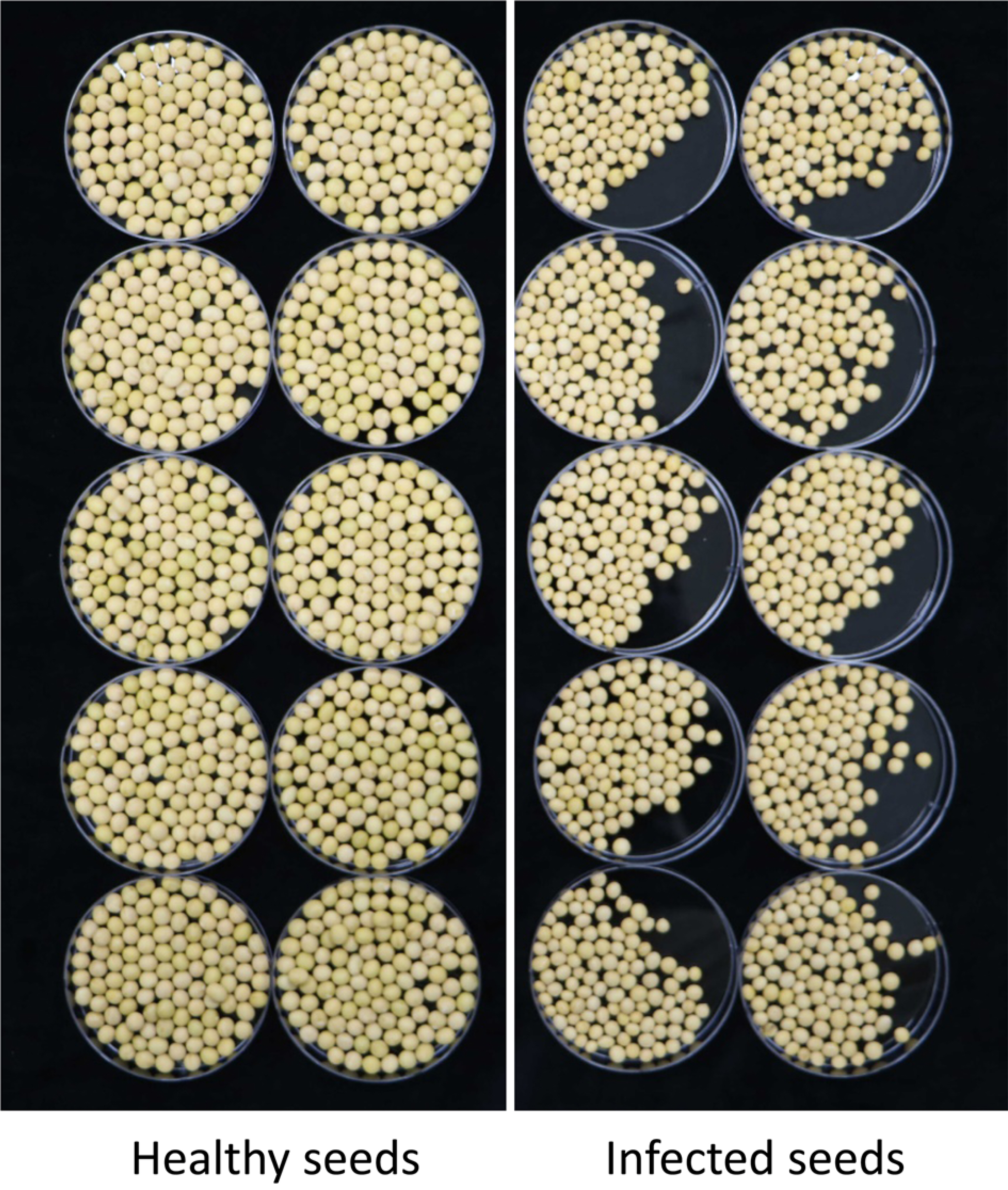

Fig. 10
Effect of the disease caused by Macrophomina phaseolina on the quality of harvested soybeans. (A) Weight of 100 seeds harvested from healthy and infected soybeans. (B) Distribution of soybean grains classified according to the diameter of grains (top, infected seed; B, healthy seed). The weight of 100 seeds was the average of 10 replications. The different letters on the bars are statistically significant based on Duncan multiple range test (P≤0.01).
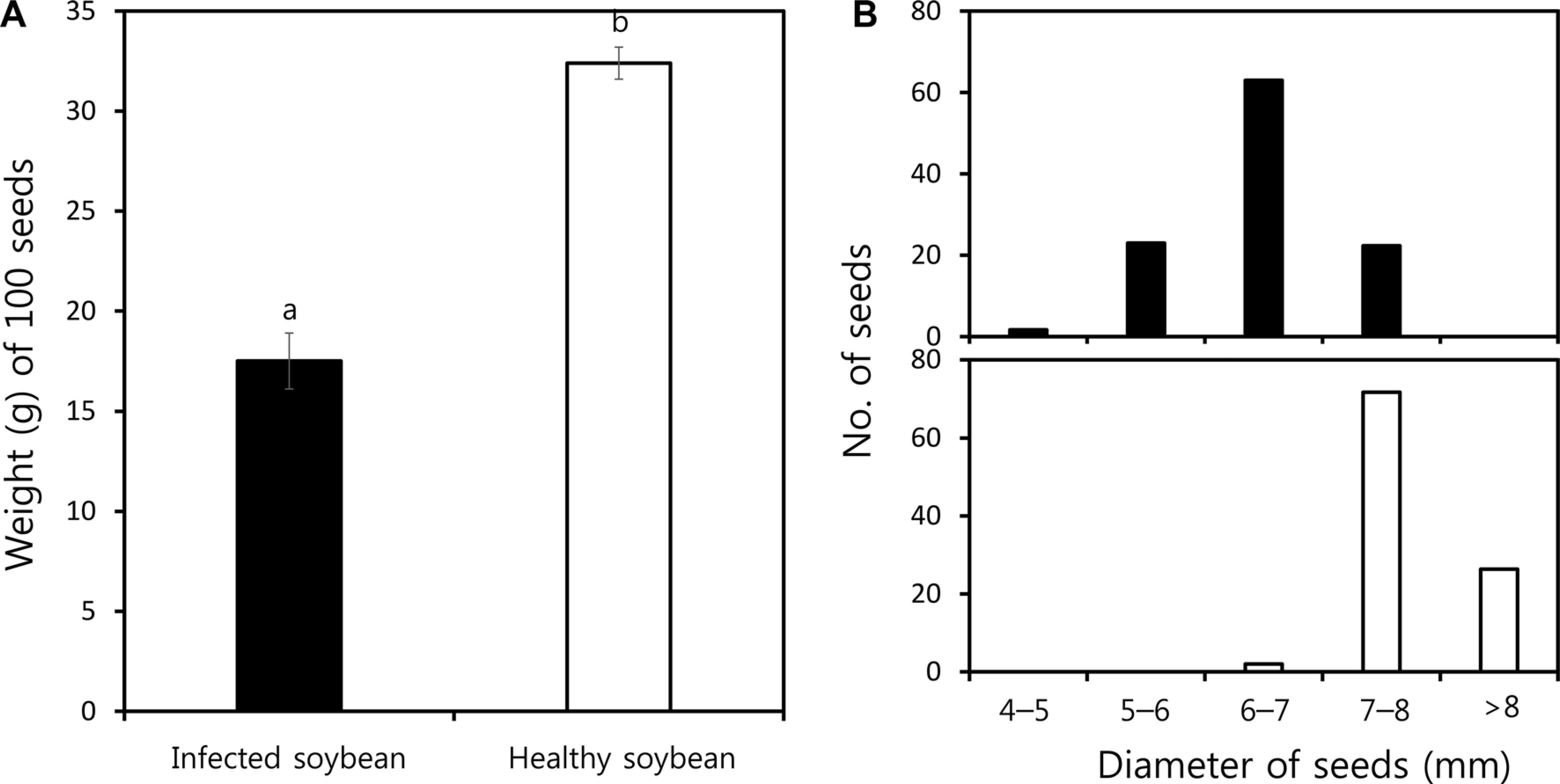
Table 1
Isolationa of pathogens in several kinds of diseased crop plants collected from the fields
| Pathogens | Soybean | Sesame | Adzuki bean | Mung bean | Peanut | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macrophomina | 16 | 4 | 1 | - b | - | 21 |
| Phomopsis | 40 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 48 |
| Colletotrichum | 29 | 5 | 3 | 3 | - | 40 |
| Botryospaeria | 11 | 2 | 1 | - | - | 14 |
| Fusarium | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 2 |
| Other | 9 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | 13 |
| Total | 105 | 15 | 11 | 5 | 2 | 138 |
References
Allen, T. W., Bradley, C. A., Sisson, A. J., Byamukama, E., Chilvers, M. I., Coker, C. M. et al. 2017. Soybean yield loss estimates due to diseases in the United States and Ontario, Canada, from 2010 to 2014. Plant Health Prog 18: 19-27.
Chidambaram, P. and Mathur, S. B. 1975. Production of pycnidia by Macrophomina phaseolina
. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc 64: 165-168.

Cummings, J. A. and Bergstrom, G. C. 2013. First report of charcoal rot caused by Macrophomina phaseolina in soybean in New York. Plant Dis 97: 1506

los Santos, B., Aguado, A., Borrero, C., Viejobueno, J. and Avilés, M. 2019. First report of charcoal rot, caused by Macrophomina phaseolina, on blueberry in southwestern Spain. Plant Dis 103: 2677

Gogoi, R., Hooda, K. S., Rai, S. N., Kumar, A. and Hossain, F. 2016. Rapid screening technique for evaluation of maize genotypes against stalk rot complex caused by Macrophomina phaseolina and Fusarium verticilloides
. Indian J. Agric. Sci 86: 1024-1030.
Gupta, G. K., Sharma, S. K. and Ramteke, R. 2012. Biology, epidemiology and management of pathogenic fungus Macrophomina phaseolina (Tassi) Goid with special reference to charcoal rot of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill). J. Phytopathol 160: 167-180.

Korea Meteorological Administration. 2020. URL https://data.kma.go.kr/stcs/grnd/grndTaList.do?pgmNo=70
[26 February 2020].
Korean Society of Plant Pathology. 2009. List of Plant Disease in Korea. 5th ed. Korean Society of Plant Pathology, Seoul, Korea. pp. 853 pp.
Korea Statistical Information Service. 2020. URL http://kosis.kr/index/index.do
[26 February 2020].
Short, G. E., Wyllie, T. D. and Bristow, P. R. 1980. Survival of Macrophomina phaseolina in soil and in residue of soybean. Phytopathology 70: 13-17.

Smith, G. S. and Wyllie, T. D. eds. by G. L. Hartman, J. B. Sinclair and J. C. Rupe, 1999. Charcoal rot. In: Compendium of Soybean Diseases, American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul, MN, USA. pp. 29-31.
Sun, S.-L., Zhu, Z.-D., Duan, C.-X., Zhao, P., Sun, F., Deng, D. et al. 2019. First report of charcoal rot caused by Macrophomina phaseolina on faba bean in China. Plant Dis 103: 1415

Sung, J. M., Park, J. H., Lee, S. C. and Chung, B. K. 1980. The outbreak and propagule formation of black root rot caused by Calonectria crotalariae in Korea. Korean J. Plant Prot 19: 228-233. (In Korean)
Kaur, S., Dhillon, G. S., Brar, S. K., Vallad, G. E. and Chauhan, V. B. 2012. Emerging phytopathogen Macrophomina phaseolina: biology, economic importance and current diagenostic trends. Crit. Rev. Microbiol 38: 136-151.


Twizeyimana, M., Hill, C. B., Pawlowski, M., Paul, C. and Hartman, G. L. 2012. A cut-stem inoculation technique to evaluate soybean for resistance to. Macrophomina phaseolina. Plant Dis 96: 1210-1215.
Wrather, J. A., Anderson, T. R., Arsyad, D. M., Gai, J., Ploper, L. D., Porta-Puglia, A. et al. 1997. Soybean disease loss estimates for the top 10 soybean producing countries in 1994. Plant Dis 81: 107-110.


Yu, S. H. 1980.
Macrophomina phaseolina detected in seeds of Sesamum indicum and it's pathogenicity. Plant Prot 19: 135-140.
Yu, S. H. and Park, J. S. 1982. Survey on seed-borne fungi in some important crops of Korea. Res. Rep. Agric. Sci. Technol. Chungnam Natl. Univ 9: 275-283. (In Korean)
Yum, K. J. and Park, E. W. 1989. Occurrence and distribution of soybean seed-borne fungi in Korea. Korean J. Plant Pathol 5: 287-293. (In Korean)
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- Related articles
-
First Report of Soft Rot Induced by Dickeya dadantii on Euphorbia hypogaea in Korea2024 March;30(1)



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



