Cho, D.-H, Kang, J. Y and Yu, Y.-H 2004. Anastomosis group, pathogenicity and growth characteristics of
Rhizoctonia solani causing damping-off on
Panax ginseng.
J. Ginseng Res 28: 183-190.

Cretoiu, M. S, Korthals, G. W, Visser, J. H. M and van Elsas, J. D 2013. Chitin amendment increases soil suppressiveness toward plant pathogens and modulates the actinobacterial and oxalobacteraceal communities in an experimental agricultural field.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol 79: 5291-5301.


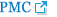
Ha, W. J, Kim, Y. C, Jung, H and Park, S. K 2014. Control of the rootknot nematode (
Meloidogyne spp.) on cucumber by a liquid bio-formulation containing chitinolytic bacteria, chitin and their products.
Res. Plant Dis 20: 112-118. In Korean

Kim, D. G, Lee, S. G, Lee, Y. K, Lee, J. P and Jung, K. C 2004. Root rot of
Panax ginseng caused by
Serratia liquefaciens.
Res. Plant Dis 10: 8-12. In Korean

Kim, D. W, Kim, H. J, Park, J. S, Kim, D. H, Cheong, S. S and Ryu, J 2010a. Selection of suitable organic matter for To-jik nursery in Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer. Korean J. Medicinal Crop Sci 18: 74-78.
Kim, Y. C, Jung, H, Kim, K. Y and Park, S. K 2008. An effective biocontrol bioformulation against Phytophthora blight of pepper using growth mixtures of combined chitinolytic bacteria under different field conditions.
Eur. J. Plant Pathol 120: 373-382.

Kim, Y. C, Lee, J. H, Bae, Y. S, Sohn, B. K and Park, S. K 2010b. Development of effective environmentally-friendly approaches to control Alternaria blight and anthracnose diseases of Korean ginseng.
Eur. J. Plant Pathol 127: 443-450.

Kim, Y. C, Kang, B. R, Kim, Y. H and Park, S. K 2017. An effective and practical strategy for biocontrol of plant diseases using on-site mass cultivation of chitin-degrading bacteria.
Res. Plant Dis 23: 19-34. In Korean

Lee, S.-G 2004.
Fusarium species associated with ginseng (
Panax ginseng) and their role in the root-rot of ginseng plant.
Res. Plant Dis 10: 248-259.

Lee, S. Y, Song, J, Park, K. H, Weon, H. Y, Kim, J. J and Han, J. H 2016. Biocontrol of ginseng damping-off by Bacillus velezensis CC112. Kor. J. Mycol 44: 176-183.
Lim, J.-S, Park, K.-C, Yun, E.-J and Choi, D.-C 2017. Analysis of economic effects for organic cultivation in
Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer.
J. Korean Soc. Int. Agric 29: 160-171.

Park, H. W, Song, J. H, Kwon, K. B, Lee, U. H and Son, H. J 2017. Growth characteristics of ginseng seedling transplanting by self soil nursery, nursery or hydroponic culture on main field.
Korean J. Medicinal Crop Sci 25: 238-243.

Reeleder, R. D and Brammall, R. A 1994. Pathogenicity of
Pythium species,
Cylindrocarpon destructans, and
Rhizoctonia solani to ginseng seedlings in Ontario.
Can. J. Plant Pathol 16: 311-316.

Seo, C. C, Jung, H. C and Park, S. K 2007. Control of powdery mildew of pepper using culture solutions of chitinolytic bacteria,
Chromobacterium sp. and
Lysobacter enzymogenes.
Res. Plant Dis 13: 40-44. In Korean

Sharp, R. G 2013. A review of the applications of chitin and its derivatives in agriculture to modify plant-microbial interactions and improve crop yields.
Agronomy 3: 757-793.

Shibuya, N and Minami, E 2001. Oligosaccharide signalling for defence responses in plant.
Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol 59: 223-233.

Shin, J.-H, Yun, B.-D, Kim, H.-J, Kim, S.-J and Chung, D.-Y 2012. Soil environment and soil-borne plant pathogen causing root rot disease of ginseng.
Korean J. Soil Sci. Fert 45: 370-376. In Korean

Williams-Woodward, J. L and DeMott, M. E 2014. Fungicide resistance in
Pythium and
Phytophthora from ornamentals in Georgia.
Acta Hortic 1055: 453-456.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print






